NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, or IXPE, is a space observatory that launched on December 9, 2021, on a Falcon 9 rocket from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is NASA’s first mission dedicated to measuring the polarization of X-rays from some of the most extreme and mysterious objects in the universe, such as black holes, neutron stars, pulsars, and supernova remnants.
Table of Contents
What is X-ray Polarization and Why is it Important?
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, like visible light, but with much higher energy and shorter wavelength. Polarization is a property of electromagnetic radiation that describes the direction of its electric and magnetic fields.
By measuring the polarization of X-rays, scientists can learn more about the structure and behavior of the objects that produce them, such as the shape and orientation of the accretion disks around black holes, the magnetic fields of neutron stars, and the geometry of pulsar jets.
X-ray polarization also helps answer fundamental questions about these turbulent and extreme environments, where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. For example, X-ray polarization can test how black holes spin and how they affect the space-time around them. It can also investigate how matter behaves under extreme conditions of density, temperature, and pressure.
How Does IXPE Work?
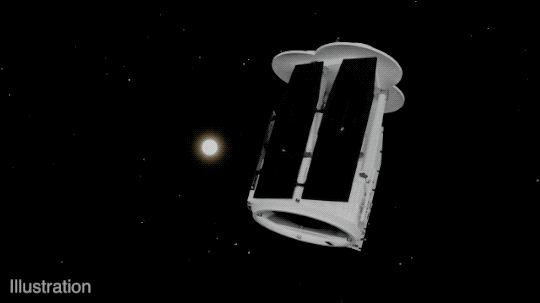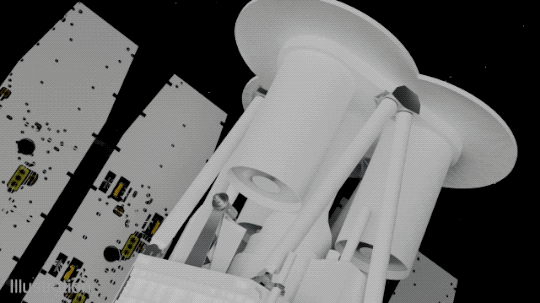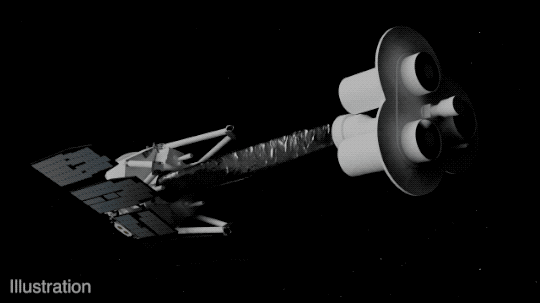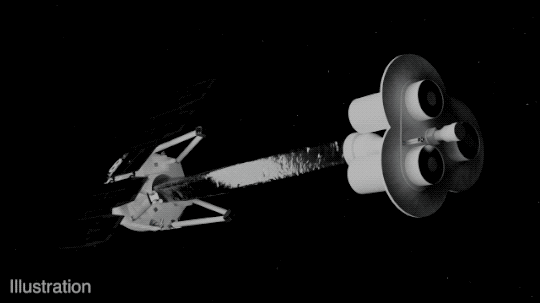
IXPE consists of three identical space telescopes, each with a mirror and a detector. The mirrors collect and focus the X-rays from the target sources, and the detectors measure the amount and direction of polarization of the X-rays.
The detectors use a special technology called gas pixel detectors, which were developed by the Italian Space Agency, one of the partners of the mission. The gas pixel detectors consist of a thin layer of gas that ionizes when hit by X-rays, creating an electric signal that is recorded by a pixelated sensor. The sensor can measure the angle and energy of the incoming X-rays, as well as the direction of polarization.
IXPE orbits the Earth at an altitude of about 540 kilometers, with an inclination of 0 degrees, meaning that it stays close to the equator. This orbit minimizes the exposure to the Earth’s radiation belts, which can interfere with the X-ray measurements.
IXPE has a mission duration of two years, during which it will observe about 40 different targets, including active galactic nuclei, microquasars, pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars, accreting X-ray binaries, supernova remnants, and the Galactic center.
What are the Expected Results and Benefits of IXPE?

Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer is expected to provide new and unprecedented information about the X-ray universe, revealing new phenomena and insights that were previously inaccessible. Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer will build on the findings of previous and current X-ray missions, such as NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and NuSTAR, by adding a new dimension of polarization to the existing measurements of position, intensity, spectrum, and timing.
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer will also complement the observations of other missions that study different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, such as NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer will advance our knowledge and understanding of the physics and astrophysics of the most extreme and exotic objects in the universe, as well as the origin and evolution of the universe itself. Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer will also contribute to the development and innovation of X-ray polarimetry technology, which has potential applications in other fields, such as medicine, industry, and security.
Conclusion
NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer mission is a groundbreaking and exciting endeavor that will explore the polarized X-ray universe and uncover the secrets of some of the most extreme and mysterious objects in the universe. Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer is NASA’s first mission dedicated to measuring the polarization of X-rays from sources such as black holes, neutron stars, pulsars, and supernova remnants.
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer launched on December 9, 2021, and consists of three identical space telescopes with gas pixel detectors that measure the amount and direction of polarization of X-rays. Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorerwill provide new and unprecedented information about the structure and behavior of these objects, as well as the physics and cosmology of these extreme environments. Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer will also advance the technology and innovation of X-ray polarimetry, which has potential applications in other fields.
FAQ About IXPE
What is NASA’s IXPE mission?
NASA’s IXPE mission, short for Imaging X-Ray Polarimetry Explorer, aims to study the polarization of X-rays emitted by astronomical objects such as black holes and neutron stars. It will provide valuable insights into the high-energy processes occurring in the universe.
What are the objectives of the IXPE mission?
The primary objectives of NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer mission are to measure the polarization of cosmic X-ray sources, improve our understanding of extreme astrophysical phenomena, and investigate the properties of magnetic fields in cosmic environments.
How will the IXPE mission contribute to scientific research?
Through its precise measurements of X-ray polarization, the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer mission will enable scientists to enhance their understanding of the physical mechanisms driving cosmic X-ray emission. This knowledge will advance our comprehension of black holes, pulsars, and other celestial objects, ultimately expanding our understanding of the universe.
When did the IXPE mission launch ?
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, or IXPE, spacecraft onboard from Launch Complex 39A, Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
How will the IXPE mission benefit the general public?
The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer mission’s findings will contribute to our collective knowledge of the universe, pushing the boundaries of astrophysics. These advancements have the potential to inspire future generations of scientists and engineers, while also fostering a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the cosmos among the general public.
For more information about IXPE, visit: IXPE Overview or IXPE Mission Page
I hope you find this article helpful. Please let me know if you have any feedback or questions. 😊





